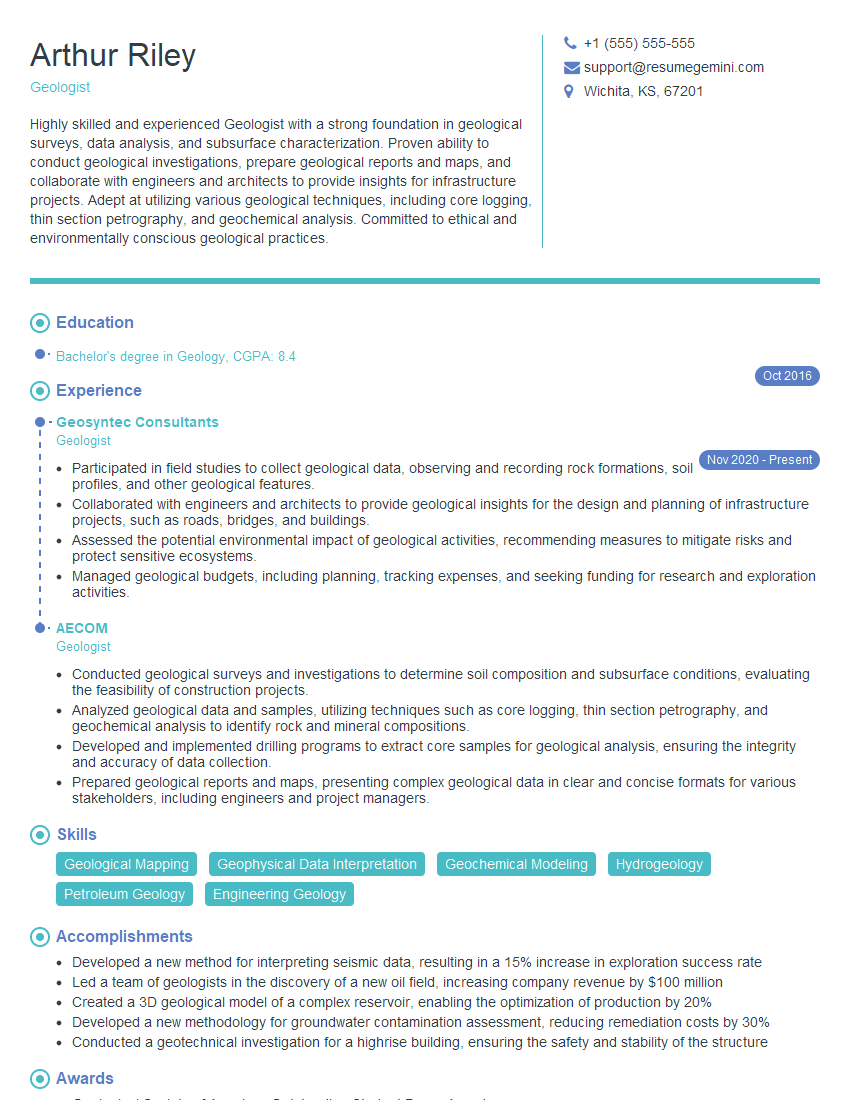
Are you gearing up for an interview for a Geologist position? Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just stepping into the role, understanding what’s expected can make all the difference. In this blog, we dive deep into the essential interview questions for Geologist and break down the key responsibilities of the role. By exploring these insights, you’ll gain a clearer picture of what employers are looking for and how you can stand out. Read on to equip yourself with the knowledge and confidence needed to ace your next interview and land your dream job!
Acing the interview is crucial, but landing one requires a compelling resume that gets you noticed. Crafting a professional document that highlights your skills and experience is the first step toward interview success. ResumeGemini can help you build a standout resume that gets you called in for that dream job.
Essential Interview Questions For Geologist
1. What is the process of identifying and classifying rocks?
The process of identifying and classifying rocks involves several steps:
- Observing physical properties: Examining the rock’s appearance, color, texture, grain size, and other physical characteristics.
- Chemical analysis: Determining the chemical composition of the rock using techniques like X-ray fluorescence or atomic absorption spectroscopy.
- Mineralogical analysis: Identifying the minerals present in the rock using methods such as petrographic microscopy or X-ray diffraction.
- Classification: Assigning the rock to a specific category based on its composition, texture, and origin, using established geological classifications (e.g., igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic).
2. Explain the principles of stratigraphy and how they are used in geological mapping?
Principles of Stratigraphy
- Law of Superposition: Younger layers of rock are typically deposited on top of older layers.
- Principle of Original Horizontality: Sedimentary rocks are initially deposited in horizontal layers.
- Law of Cross-Cutting Relationships: Faults and intrusions are younger than the rocks they intersect.
Geological Mapping
- By identifying and correlating rock units based on their stratigraphic relationships, geologists can create geological maps that depict the distribution and ages of different rocks in an area.
- These maps provide insights into geological history, structure, and resource potential.
3. Describe the different types of geological structures and how they can be identified in the field.
Geological structures are features in the Earth’s crust that result from deformation and movement of rocks.
- Folds: Bends or curves in rock layers.
- Faults: Fractures in rock where displacement has occurred.
- Joints: Fractures in rock that lack displacement.
- Unconformities: Surfaces representing gaps in the geological record.
- These structures can be identified in the field based on their characteristic patterns, orientations, and relationships to surrounding rocks.
4. How do you determine the relative ages of rocks in a sequence?
To determine the relative ages of rocks in a sequence, geologists use several methods:
- Stratigraphic relationships: Identifying the order in which rock layers were deposited, based on the principles of stratigraphy.
- Cross-cutting relationships: Determining which rocks are older or younger based on their intersections with other geological features (e.g., faults, intrusions).
- Fossil evidence: Using fossils to establish the age of sedimentary rocks, as different fossils are associated with specific geological periods.
- Radiometric dating: Using radioactive decay to determine the absolute age of rocks, which can be used to cross-check and refine relative age determinations.
5. Explain the concept of groundwater flow and how it relates to hydrogeology.
Groundwater flow refers to the movement of water through the pores and fractures of rock formations below the Earth’s surface.
- Darcy’s Law: Describes the relationship between the hydraulic conductivity of the rock, the hydraulic gradient, and the velocity of groundwater flow.
- Aquifers: Rock formations that store and transmit groundwater.
- Hydrogeology: The study of groundwater flow and its interactions with the geological environment, including groundwater resources, contamination, and modeling.
6. How do you assess the stability of a slope and identify potential hazards?
Assessing slope stability involves considering several factors:
- Geological conditions: Rock and soil type, structure, and groundwater conditions.
- Slope geometry: Angle of the slope, height, and length.
- Vegetation cover: Type and density of vegetation, which can contribute to slope stability.
- Human activities: Construction, mining, and agriculture can modify slope conditions and increase hazards.
- Slope stability analysis: Using geotechnical techniques to calculate the factor of safety and identify potential failure mechanisms.
7. What is the role of a geologist in environmental impact assessments?
Geologists play a crucial role in environmental impact assessments (EIAs) by:
- Site characterization: Assessing the geological and hydrogeological conditions of the proposed project area.
- Hazard identification: Identifying potential geological hazards such as landslides, earthquakes, or contamination.
- Mitigation measures: Developing and recommending measures to mitigate geological hazards and protect the environment.
- Monitoring: Monitoring geological conditions during and after project implementation to ensure compliance and effectiveness of mitigation measures.
8. How do you use GIS (Geographic Information Systems) in your geological work?
GIS is a powerful tool for geologists, enabling them to:
- Data management: Storing, organizing, and managing geological data, such as maps, rock samples, and geophysical data.
- Spatial analysis: Analyzing spatial relationships between geological features, such as proximity to faults or groundwater aquifers.
- Mapping and visualization: Creating geological maps, cross-sections, and 3D models to visualize and communicate geological information.
- Modeling: Using GIS to develop models of geological processes, such as groundwater flow or slope stability.
9. What are the emerging trends and technologies in the field of geology?
The field of geology is constantly evolving, and some emerging trends and technologies include:
- Remote sensing and satellite imagery: Using satellite data to map geological features and monitor environmental changes.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): High-resolution 3D mapping technology for terrain analysis and geological hazard assessment.
- Geophysical methods: Advanced geophysical techniques, such as seismic imaging and electrical resistivity tomography, for subsurface exploration and characterization.
- Data science and machine learning: Using machine learning algorithms to analyze large geological datasets and identify patterns and relationships.
10. How do you stay updated with the latest advancements in geology?
To stay updated with the latest advancements in geology, I:
- Attend conferences and workshops: Network with other professionals and learn about the latest research and best practices.
- Read scientific journals and publications: Subscribe to geological journals and regularly review articles to keep abreast of new discoveries and developments.
- Participate in professional organizations: Join geological societies and attend their meetings and webinars to connect with the community and stay informed.
- Take continuing education courses: Enroll in online or in-person courses to expand my knowledge and skills in specific areas of geology.
Interviewers often ask about specific skills and experiences. With ResumeGemini‘s customizable templates, you can tailor your resume to showcase the skills most relevant to the position, making a powerful first impression. Also check out Resume Template specially tailored for Geologist.
Career Expert Tips:
- Ace those interviews! Prepare effectively by reviewing the Top 50 Most Common Interview Questions on ResumeGemini.
- Navigate your job search with confidence! Explore a wide range of Career Tips on ResumeGemini. Learn about common challenges and recommendations to overcome them.
- Craft the perfect resume! Master the Art of Resume Writing with ResumeGemini’s guide. Showcase your unique qualifications and achievements effectively.
- Great Savings With New Year Deals and Discounts! In 2025, boost your job search and build your dream resume with ResumeGemini’s ATS optimized templates.
Researching the company and tailoring your answers is essential. Once you have a clear understanding of the Geologist‘s requirements, you can use ResumeGemini to adjust your resume to perfectly match the job description.
Key Job Responsibilities
Geologists are responsible for studying the physical structure of the earth, including its rocks, minerals, and fossils. They also study the processes that have shaped the earth over time, and how these processes have affected the environment and human activities.
1. Conduct field studies
Geologists conduct field studies to collect data about the earth’s physical structure. They may study rock formations, fossils, and other geological features to learn about the history of the earth and the processes that have shaped it.
- Plan and conduct field studies to collect data on geological formations and processes.
- Use a variety of field equipment, including GPS, compasses, and rock hammers, to collect data.
2. Analyze data
Geologists analyze data collected from field studies to learn about the earth’s history and the processes that have shaped it. They may use computer models and other tools to analyze data and draw conclusions.
- Analyze data from field studies to determine the geological history of an area.
- Use computer models and other tools to analyze data and draw conclusions.
3. Write reports
Geologists write reports to communicate their findings to other scientists, policymakers, and the public. Reports may include information about the earth’s history, the processes that have shaped it, and the potential impacts of human activities on the environment.
- Write reports to communicate findings to other scientists, policymakers, and the public.
- Present findings at conferences and other professional gatherings.
4. Other responsibilities
Geologists may also be responsible for other tasks, such as teaching, consulting, or working with environmental groups.
- Teach courses in geology at colleges and universities.
- Consult with businesses and governments on geological issues.
- Work with environmental groups to protect natural resources.
Interview Tips
Interviewing for a geologist position can be a challenging experience. However, by following these tips, you can increase your chances of success.
1. Research the company and the position
Before you go on an interview, it is important to research the company and the position you are applying for. This will help you to understand the company’s culture and the specific requirements of the position.
- Visit the company’s website to learn about its history, mission, and values.
- Read the job description carefully to understand the specific requirements of the position.
2. Prepare answers to common interview questions
There are a number of common interview questions that you can expect to be asked, such as “Why are you interested in this position?” and “What are your strengths and weaknesses?”. It is important to prepare answers to these questions in advance so that you can deliver them confidently and concisely.
- Practice answering common interview questions with a friend or family member.
- Be prepared to talk about your education, experience, and skills.
3. Be yourself
It is important to be yourself during an interview. The interviewer wants to get to know the real you, so don’t try to be someone you’re not.
- Be honest and genuine in your answers.
- Don’t be afraid to show your personality.
4. Follow up
After the interview, it is important to follow up with the interviewer. This shows that you are interested in the position and that you appreciate their time. email the interviewer to thank them for their time and reiterate your interest in the position.
- Send a thank-you note to the interviewer within 24 hours of the interview.
- Reiterate your interest in the position and why you are a good fit for the company.
Next Step:
Armed with this knowledge, you’re now well-equipped to tackle the Geologist interview with confidence. Remember, a well-crafted resume is your first impression. Take the time to tailor your resume to highlight your relevant skills and experiences. And don’t forget to practice your answers to common interview questions. With a little preparation, you’ll be on your way to landing your dream job. So what are you waiting for? Start building your resume and start applying! Build an amazing resume with ResumeGemini.