Are you gearing up for a career shift or aiming to ace your next interview? Look no further! We’ve curated a comprehensive guide to help you crack the interview for the coveted Tool and Die Designer position. From understanding the key responsibilities to mastering the most commonly asked questions, this blog has you covered. So, buckle up and let’s embark on this journey together
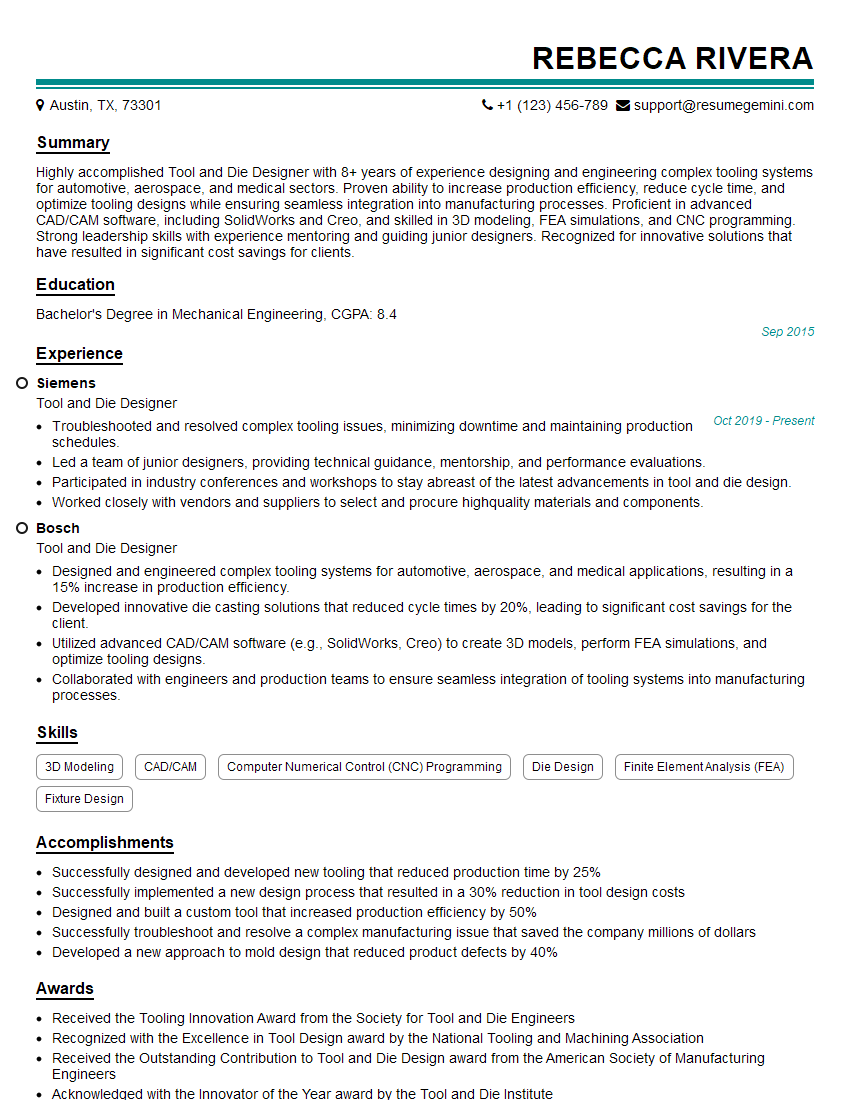
Acing the interview is crucial, but landing one requires a compelling resume that gets you noticed. Crafting a professional document that highlights your skills and experience is the first step toward interview success. ResumeGemini can help you build a standout resume that gets you called in for that dream job.
Essential Interview Questions For Tool and Die Designer
1. Explain the process of designing a mold for a plastic injection molding process?
The process of designing a mold for a plastic injection molding process involves several key steps:
- Part Design: Analyze the part geometry and identify critical dimensions, tolerances, and material requirements.
- Mold Base Selection: Choose an appropriate mold base size and type based on the part size, shape, and production volume.
- Gating System Design: Design the gates, runners, and sprues to ensure proper plastic flow and minimize defects.
- Cooling System Design: Incorporate cooling channels to regulate mold temperature and prevent part distortion.
- Ejection System Design: Determine the appropriate ejection mechanism (e.g., pins, blades, or strippers) to safely eject the molded part.
- Mold Manufacturing: Use computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) to generate toolpaths and fabricate the mold components.
- Mold Assembly and Testing: Assemble the mold components, conduct trial runs, and make adjustments to optimize performance.
2. What are the key factors to consider when designing a die for a metal stamping process?
Material Selection and Properties
- Consider the material’s strength, hardness, thickness, and ductility to withstand the stamping forces and maintain dimensional accuracy.
- Evaluate the material’s surface finish and coating requirements for aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
Die Design
- Design the cutting edges of the die to achieve clean cuts and minimize burrs.
- Incorporate clearances for material deformation and prevent jamming.
- Provide adequate support to prevent die deflection and ensure part accuracy.
Press Selection and Setup
- Determine the required press tonnage and stroke based on the material thickness and part geometry.
- Ensure proper die alignment and lubrication to minimize wear and tear.
3. How do you optimize a stamping die for high-volume production?
- Progressive Die Design: Create a series of stages in the die to perform multiple operations sequentially, increasing productivity.
- Automated Material Feeding and Part Ejection: Integrate automatic systems to reduce manual handling and increase efficiency.
- Die Cooling and Lubrication: Implement temperature control and lubrication systems to minimize wear and tool life.
- Quality Control Integration: Incorporate in-process inspection techniques to ensure part quality and reduce scrap rates.
- Preventative Maintenance and Repair: Establish a regular maintenance schedule to prolong die life and minimize downtime.
4. Describe the different types of mold materials used in injection molding and their advantages and disadvantages.
- Steel: Durable, high-strength, and resistant to wear; expensive and requires heat treatment.
- Aluminum: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and good thermal conductivity; less durable than steel and prone to deformation.
- Beryllium Copper: Excellent wear resistance, high thermal conductivity, and high strength; expensive and requires special handling.
- P-20 Tool Steel: General-purpose steel with good hardness, wear resistance, and dimensional stability.
- H-13 Tool Steel: High-carbon, high-chromium steel with excellent wear resistance and toughness.
5. What are the different types of surface treatments applied to dies and molds?
- Nitriding: Improves surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
- Carburizing: Increases surface hardness and strength by adding carbon to the steel.
- Hard Chrome Plating: Provides high wear resistance and corrosion protection.
- Electroless Nickel Plating: Improves corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and release properties.
- Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Creates thin, hard coatings with high wear resistance and low friction.
6. How do you use computer-aided design (CAD) software in your tool and die design process?
- Part Modeling: Create 3D models of the part to be manufactured.
- Mold/Die Design: Develop virtual models of the mold or die components.
- Simulation: Analyze the mold/die design for potential issues, such as material flow, stress distribution, and ejection.
- CAM Programming: Generate toolpaths for mold/die manufacturing.
- Documentation: Create drawings, assembly instructions, and other documentation.
7. What are the industry standards and regulations that apply to tool and die design?
- ANSI Standards: American National Standards Institute (ANSI) sets standards for tool and die design, materials, and safety.
- ASTM Standards: American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) develops standards for testing materials used in tool and die making.
- ISO Standards: International Organization for Standardization (ISO) establishes international standards for tool and die design and manufacturing.
- OSHA Regulations: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets safety regulations for tool and die shops.
8. Describe your experience in using rapid prototyping techniques to create prototypes of molds and dies.
- Stereolithography (SLA): Creating 3D models by curing liquid resin with UV light.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Fusing powdered material layer by layer to build 3D models.
- 3D Printing: Creating 3D models by depositing molten material layer by layer.
- Benefits of Rapid Prototyping:
- Faster and cheaper than traditional prototyping methods.
- Ability to test design concepts before investing in mold/die manufacturing.
- Reduces lead times and improves product development efficiency.
9. How do you stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in tool and die design and manufacturing technology?
- Industry Publications: Reading trade magazines and journals.
- Conferences and Trade Shows: Attending industry events to learn about new technologies and best practices.
- Online Resources: Utilizing online forums, websites, and webinars to stay informed.
- Continuing Education: Taking courses or workshops to enhance skills and knowledge.
- Networking: Connecting with other tool and die designers and engineers to exchange ideas and learn from their experiences.
10. Describe a challenging tool or die design project you have worked on and how you overcame the challenges.
- Project Description: Briefly describe the project, including the part to be manufactured and the specific challenges faced.
- Problem-Solving Approach: Explain the steps taken to identify and analyze the challenges.
- Solution Implementation: Describe the innovative or unconventional solutions implemented to overcome the challenges.
- Results: Highlight the positive outcomes of the project, such as improved part quality, reduced production time, or increased efficiency.
Interviewers often ask about specific skills and experiences. With ResumeGemini‘s customizable templates, you can tailor your resume to showcase the skills most relevant to the position, making a powerful first impression. Also check out Resume Template specially tailored for Tool and Die Designer.
Career Expert Tips:
- Ace those interviews! Prepare effectively by reviewing the Top 50 Most Common Interview Questions on ResumeGemini.
- Navigate your job search with confidence! Explore a wide range of Career Tips on ResumeGemini. Learn about common challenges and recommendations to overcome them.
- Craft the perfect resume! Master the Art of Resume Writing with ResumeGemini’s guide. Showcase your unique qualifications and achievements effectively.
- Great Savings With New Year Deals and Discounts! In 2025, boost your job search and build your dream resume with ResumeGemini’s ATS optimized templates.
Researching the company and tailoring your answers is essential. Once you have a clear understanding of the Tool and Die Designer‘s requirements, you can use ResumeGemini to adjust your resume to perfectly match the job description.
Key Job Responsibilities
Tool and Die Designers are experts in designing and creating tools, such as dies, molds, jigs, and fixtures used in manufacturing processes. They collaborate with engineers, manufacturers, and other professionals to ensure the precision and efficiency of the tools they create.
1. Design and Develop Tools and Dies
Using computer-aided design (CAD) software to create detailed drawings and models
- Analyzing engineering specifications and customer requirements to determine the best design for the tool or die
- Conducting simulations and testing to optimize the design and ensure its functionality
2. Collaborate with Engineers and Manufacturers
Discussing design concepts with engineers to ensure the tool or die meets the required specifications
- Working with manufacturers to select the appropriate materials and manufacturing processes for the tool or die
- Providing technical support to manufacturers during the production process
3. Oversee Tool and Die Production
Inspecting tools and dies to ensure they meet the required quality standards
- Monitoring the production process to identify and resolve any issues
- Making adjustments to the design or manufacturing process as needed
4. Maintain and Repair Tools and Dies
Performing regular maintenance and repairs on tools and dies to ensure their longevity and functionality
- Troubleshooting any issues that may arise during the use of the tool or die
- Replacing worn or damaged components
Interview Tips
Preparing for an interview for a Tool and Die Designer position requires thorough research and practice. Here are some tips to help you ace the interview:
1. Research the Company and Position
Gather information about the company’s industry, products, and culture. This will help you understand their needs and how your skills and experience can align with them.
- Visit the company’s website and social media pages to learn about their recent projects and initiatives.
- Read industry publications and news articles to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and technologies.
2. Practice Your Technical Skills
Brush up on your CAD software skills and be prepared to demonstrate your proficiency. You may also be asked to solve technical problems or discuss design concepts.
- Create a portfolio of your best work to showcase your design capabilities.
- Practice answering technical questions related to the design and manufacturing of tools and dies.
3. Highlight Your Communication and Teamwork Skills
Tool and Die Designers often work in teams and need to communicate effectively with engineers, manufacturers, and other stakeholders. Demonstrate your ability to collaborate and present your ideas clearly.
- Provide examples of projects where you successfully collaborated with others to achieve a common goal.
- Practice delivering a concise and engaging presentation about your design work.
4. Emphasize Your Problem-Solving Abilities
Discuss your experience in identifying and resolving technical issues. Tool and Die Designers need to be able to troubleshoot problems and find creative solutions.
- Describe a situation where you faced a challenge and how you overcame it.
- Explain how you analyze problems and develop effective solutions.
5. Prepare for Common Interview Questions
Some common interview questions for Tool and Die Designers include:
- Tell me about your experience in designing and developing tools and dies.
- How do you stay up-to-date on the latest design trends and technologies?
- Give me an example of a challenging project you worked on and how you overcame the obstacles.
- How do you handle working under pressure and tight deadlines?
- Why are you interested in working for our company?
Next Step:
Armed with this knowledge, you’re now well-equipped to tackle the Tool and Die Designer interview with confidence. Remember, a well-crafted resume is your first impression. Take the time to tailor your resume to highlight your relevant skills and experiences. And don’t forget to practice your answers to common interview questions. With a little preparation, you’ll be on your way to landing your dream job. So what are you waiting for? Start building your resume and start applying! Build an amazing resume with ResumeGemini.