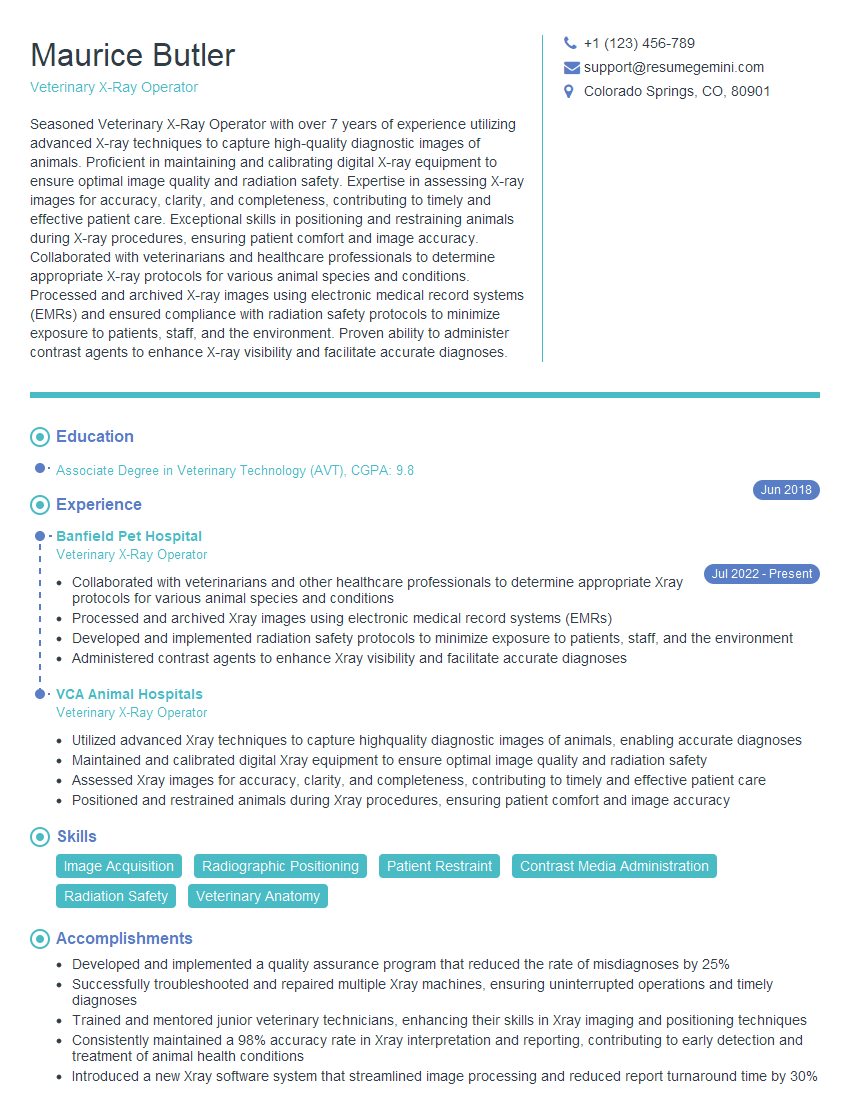
Are you gearing up for a career shift or aiming to ace your next interview? Look no further! We’ve curated a comprehensive guide to help you crack the interview for the coveted Veterinary X-Ray Operator position. From understanding the key responsibilities to mastering the most commonly asked questions, this blog has you covered. So, buckle up and let’s embark on this journey together.
Acing the interview is crucial, but landing one requires a compelling resume that gets you noticed. Crafting a professional document that highlights your skills and experience is the first step toward interview success. ResumeGemini can help you build a standout resume that gets you called in for that dream job.
Essential Interview Questions For Veterinary X-Ray Operator
1. What are the different types of X-ray equipment used in veterinary medicine?
- Fixed X-ray machines: These are large, stationary machines that are typically used in veterinary hospitals and clinics.
- Portable X-ray machines: These are smaller, more portable machines that can be used in the field or in smaller veterinary clinics.
- Computed tomography (CT) scanners: These machines use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the body, which can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions.
- Fluoroscopy machines: These machines allow veterinarians to view real-time images of the body, which can be used to guide procedures such as surgery or endoscopy.
2. What are the different types of X-ray views used in veterinary medicine?
Radiographic views
- Dorsal-ventral (DV) view: This view is taken with the animal lying on its back, and the X-ray beam is projected from above.
- Ventro-dorsal (VD) view: This view is taken with the animal lying on its stomach, and the X-ray beam is projected from below.
- Lateral view: This view is taken with the animal standing on its side, and the X-ray beam is projected from the side.
Fluoroscopic views
- Real-time imaging: This allows veterinarians to view moving images of the body, which can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions.
- Spot filming: This allows veterinarians to capture still images from the fluoroscopic video, which can be used to document findings or to create diagnostic reports.
3. What are the different factors that can affect the quality of an X-ray image?
- Patient positioning: The patient must be positioned correctly in order to obtain a clear and accurate image.
- Exposure settings: The exposure settings must be adjusted correctly in order to obtain an image that is not too dark or too light.
- Processing techniques: The X-ray film must be processed correctly in order to obtain an image that is clear and free of artifacts.
- Equipment malfunction: Equipment malfunction can also affect the quality of an X-ray image.
4. What are the different types of artifacts that can appear on an X-ray image?
- Motion artifacts: These artifacts are caused by movement of the patient or the X-ray machine during the exposure.
- Patient artifacts: These artifacts are caused by the presence of foreign objects on or in the patient, such as jewelry, hair, or bandages.
- Processing artifacts: These artifacts are caused by improper processing of the X-ray film, such as over- or under-development.
- Equipment artifacts: These artifacts are caused by malfunctioning X-ray equipment, such as a faulty X-ray tube or a dirty collimator.
5. What are the different types of X-ray contrast agents used in veterinary medicine?
- Positive contrast agents: These agents are used to make structures appear more opaque on X-ray images.
- Negative contrast agents: These agents are used to make structures appear less opaque on X-ray images.
- Water-soluble contrast agents: These agents are used to visualize the gastrointestinal tract and the urinary tract.
- Oil-soluble contrast agents: These agents are used to visualize the lungs and the heart.
6. What are the different types of X-ray safety precautions that should be taken by veterinary X-ray operators?
- Wear a lead apron and gloves when operating X-ray equipment.
- Stand behind a lead barrier when exposing X-rays.
- Limit the number of X-rays taken on a patient.
- Use the lowest possible exposure settings that will produce a diagnostic image.
- Monitor your radiation exposure regularly.
7. What are the different types of continuing education opportunities available to veterinary X-ray operators?
- Veterinary X-ray conferences and workshops
- Online veterinary X-ray courses
- Veterinary X-ray textbooks and journals
- Mentoring from experienced veterinary X-ray operators
8. What are the different types of professional organizations for veterinary X-ray operators?
- American Society of Veterinary Radiologists (ASVR)
- National Association of Veterinary Technicians in America (NAVTA)
- International Veterinary Radiology Association (IVRA)
9. What are the different types of career advancement opportunities available to veterinary X-ray operators?
- Veterinary X-ray supervisor
- Veterinary X-ray technologist
- Veterinary X-ray instructor
- Veterinary X-ray researcher
10. What are the different types of personal qualities that are important for veterinary X-ray operators?
- Attention to detail
- Good communication skills
- Patience
- Problem-solving skills
- Teamwork skills
Interviewers often ask about specific skills and experiences. With ResumeGemini‘s customizable templates, you can tailor your resume to showcase the skills most relevant to the position, making a powerful first impression. Also check out Resume Template specially tailored for Veterinary X-Ray Operator.
Career Expert Tips:
- Ace those interviews! Prepare effectively by reviewing the Top 50 Most Common Interview Questions on ResumeGemini.
- Navigate your job search with confidence! Explore a wide range of Career Tips on ResumeGemini. Learn about common challenges and recommendations to overcome them.
- Craft the perfect resume! Master the Art of Resume Writing with ResumeGemini’s guide. Showcase your unique qualifications and achievements effectively.
- Great Savings With New Year Deals and Discounts! In 2025, boost your job search and build your dream resume with ResumeGemini’s ATS optimized templates.
Researching the company and tailoring your answers is essential. Once you have a clear understanding of the Veterinary X-Ray Operator‘s requirements, you can use ResumeGemini to adjust your resume to perfectly match the job description.
Key Job Responsibilities
Veterinary X-Ray Operators are responsible for taking and processing X-ray images of animals, and assisting veterinarians in diagnosing and treating animal injuries and illnesses.
1. Taking and Processing X-Rays
Veterinary X-Ray Operators are responsible for taking high-quality X-ray images of animals.
- Position animals for X-rays, ensuring proper alignment and immobilization.
- Operate X-ray equipment, setting appropriate exposure parameters.
- Produce and process X-ray images using digital or film-based techniques.
2. Animal Handling and Restraint
Veterinary X-Ray Operators must be able to handle and restrain animals safely and humanely.
- Restrain animals using appropriate techniques and equipment, minimizing stress and discomfort.
- Maintain a safe and calm environment for animals during X-ray procedures.
3. Image Analysis and Interpretation
Veterinary X-Ray Operators assist veterinarians in interpreting X-ray images to identify abnormalities.
- Evaluate X-ray images for signs of fractures, dislocations, foreign objects, and other abnormalities.
- Provide preliminary interpretations of X-ray findings to veterinarians for further evaluation.
4. Record Keeping and Reporting
Veterinary X-Ray Operators maintain accurate records of X-ray procedures and findings.
- Record patient information, X-ray settings, and any notable observations.
- Prepare and maintain patient X-ray archives for future reference.
Interview Tips
Preparing for a Veterinary X-Ray Operator interview can increase your chances of success. Here are some tips to help you ace your interview:
1. Research the Clinic and Position
Familiarize yourself with the clinic’s services, facilities, and team.
- Visit the clinic’s website and social media pages.
- Read online reviews and testimonials from clients and former employees.
- Research the specific duties and responsibilities of the Veterinary X-Ray Operator position.
2. Practice Your Skills
Brush up on your technical skills and veterinary knowledge.
- Review your X-ray imaging and animal handling techniques.
- Practice analyzing and interpreting X-ray images.
- Study animal anatomy and common veterinary conditions.
3. Prepare Your Questions
Asking thoughtful questions demonstrates your interest and engagement.
- Inquire about the clinic’s caseload and typical procedures.
- Ask about opportunities for professional development and advancement.
- Request specific examples of how the Veterinary X-Ray Operator contributes to the veterinary team.
4. Dress Professionally and Be Punctual
Make a good first impression by dressing professionally and arriving on time for your interview.
- Wear clean, pressed clothing and comfortable shoes.
- Arrive at the clinic a few minutes early to allow time to relax and collect your thoughts.
5. Be Yourself and Be Enthusiastic
Interviews are an opportunity to showcase your skills and personality.
- Be confident and articulate when answering questions.
- Share your passion for veterinary medicine and animal care.
- Express your interest in working at the clinic and contributing to the team.
Next Step:
Now that you’re armed with the knowledge of Veterinary X-Ray Operator interview questions and responsibilities, it’s time to take the next step. Build or refine your resume to highlight your skills and experiences that align with this role. Don’t be afraid to tailor your resume to each specific job application. Finally, start applying for Veterinary X-Ray Operator positions with confidence. Remember, preparation is key, and with the right approach, you’ll be well on your way to landing your dream job. Build an amazing resume with ResumeGemini